Warning
These docs are still being developed. In the future this page will contain a very short introduction to user management in Drupal and practical examples for site administration of a Tripal site.
User Permissions
Users : Anyone who visits your website including you. There are three groups of users. anonymous users (who are not logged in), authenticated users (who are logged in) and administrative users (created when a site was installed, or User 1).
Permissions : A group of actions (example - import a GFF3 file, view/edit content and change configuration). Permissions are defined by the modules that provide the actions.
Roles : Permissions are grouped into roles, each of which can be defined and then permissions are granted. Exaample roles are Curators or Data Submittors.
Users and permissions allow you to give certain groups for example, researchers access to private data. Roles can help you setup groups of collaborators so you can assign the permission to the group as a whole which makes it easier if any one member leaves or joins the group.
Refer to https://www.drupal.org/docs/user_guide/en/user-concept.html for more details.
It is a good practice to make several roles on your Tripal site. For example, for managing biological data and knowledgebases like model organism database, you might want a Curator role that allows data curators to curate information on a specific organism using appropriate unique traceable identifiers, and providing necessary metadata including source and provenance. a set of genes, and their associated mRNA, CDS, UTRs, etc. For more information, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biocuration.
Creating Roles to enable Curation
Biocuration involves the collection, curation, annotation, validation, writing related grants, and publications and integration of information related to the biological sciences into databases or resources.
Here is a walk through creating a “Curator” role in Tripal based on a need and then assign these roles permissions by the Administrator. For example, a curator of genomic data would need access to specific importers and content types associated with the genome of the organism.
Steps
From the top menu :
Home -> Administration -> People -> Roles ->
You will find default roles Anonymous user, Authenticated user, and Administrator already present.
Create User
From the top menu :
- Home -> Administration -> People -> +Add User ->
Username : curator_user
Password : abcd_123_!@#
Roles : Content editor
Click on Create new account leaving other items as default
From the top menu -> People -> curator_user now appears in list of Usernames.
Create Roles and Assign them to Users
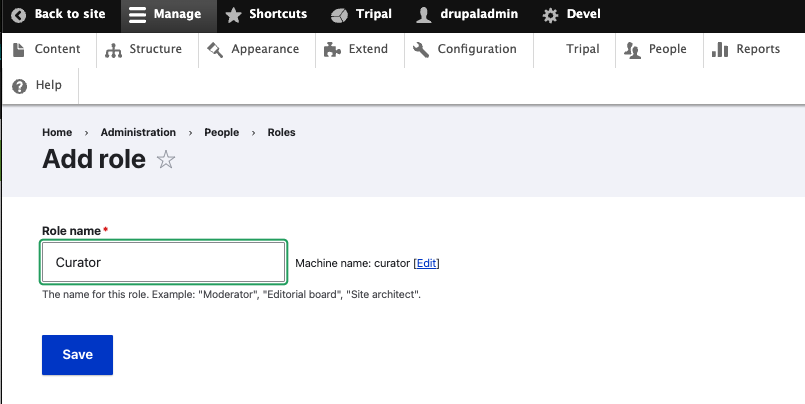
Home -> Administration -> People -> +Add Role ->
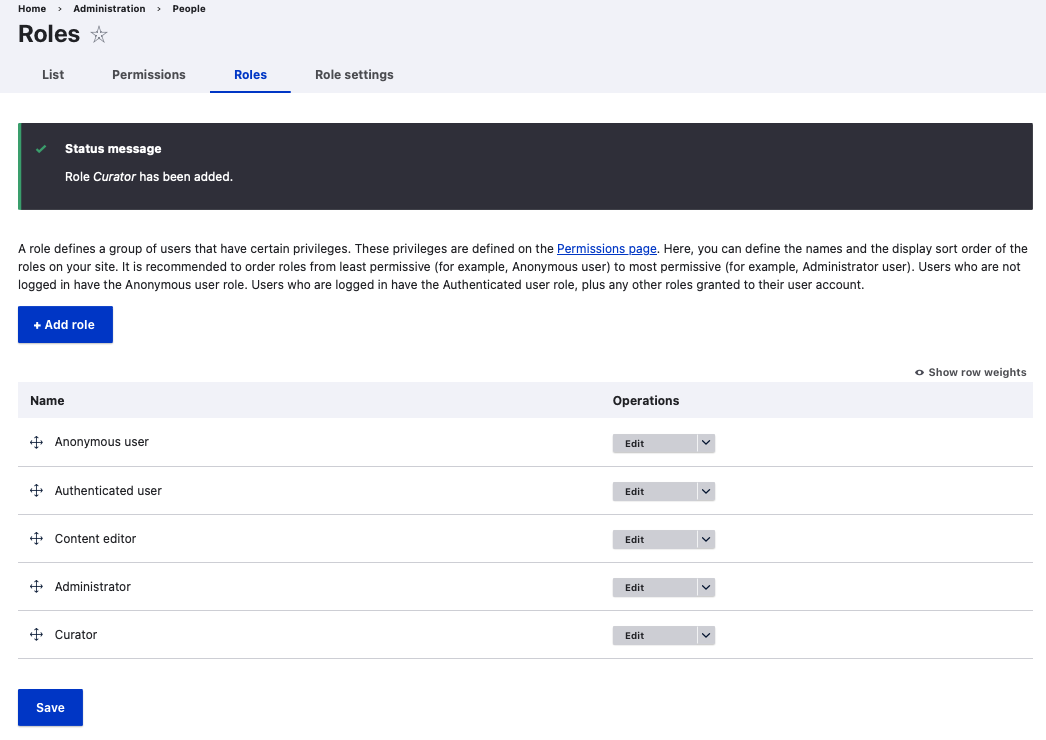
Type Curator for Role name in text box and click Save. A status message is displayed.
And you can find the Curator Role added to the list of Roles under Name.
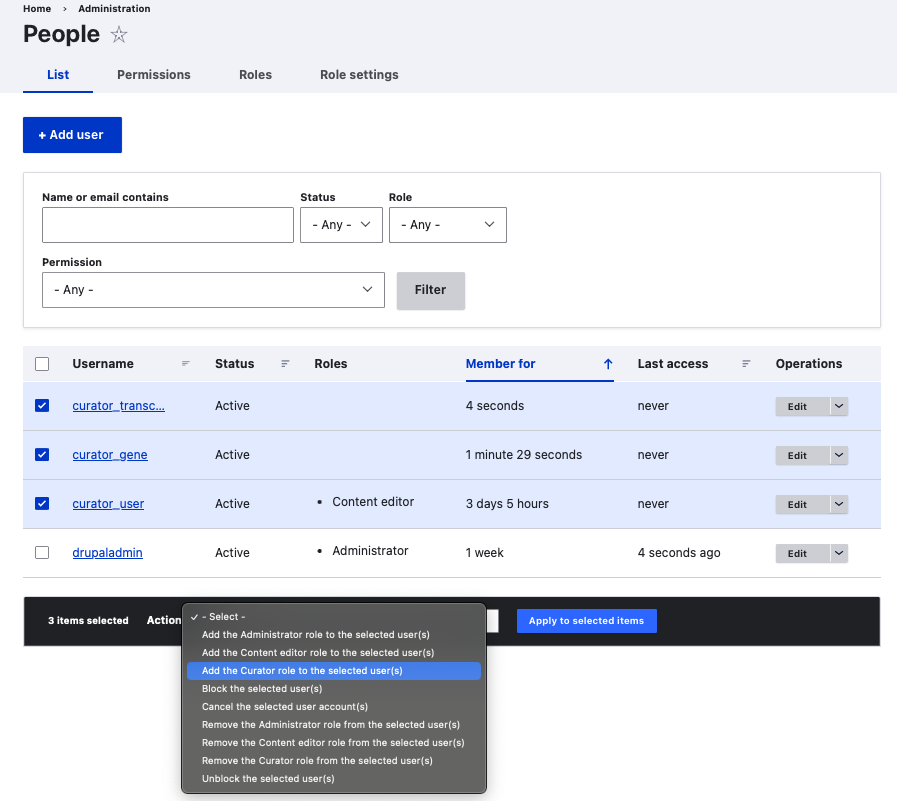
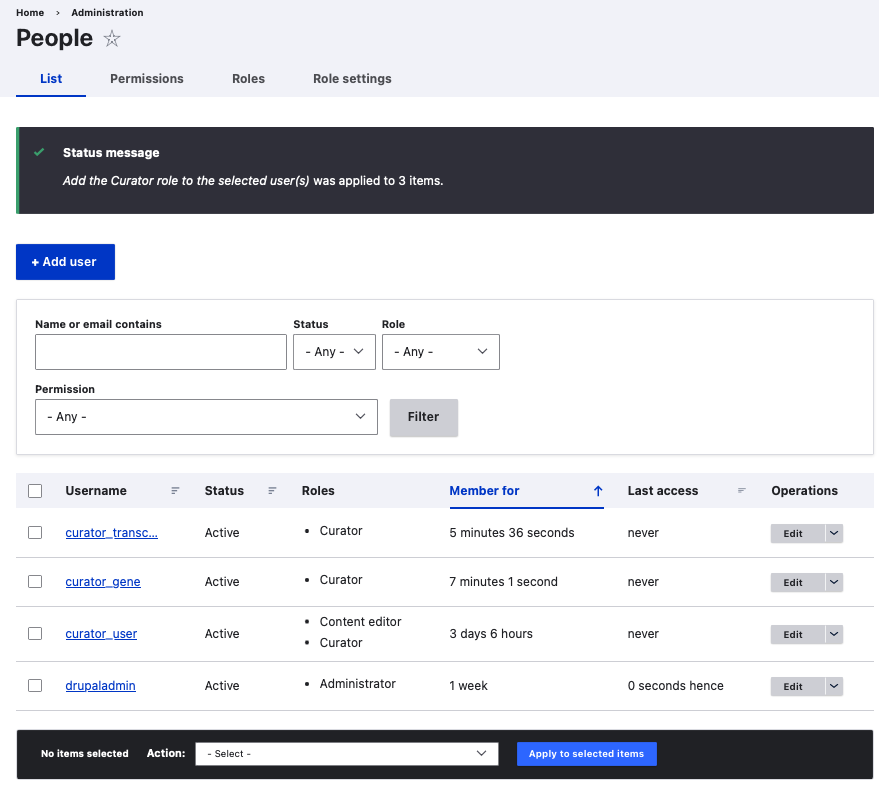
To perform same action on multiple users, for example, to add the Curator role to more than 1 user, from the top menu,
Home -> Administration -> People -> click inside checkbox before all usernames having prefix curator_.
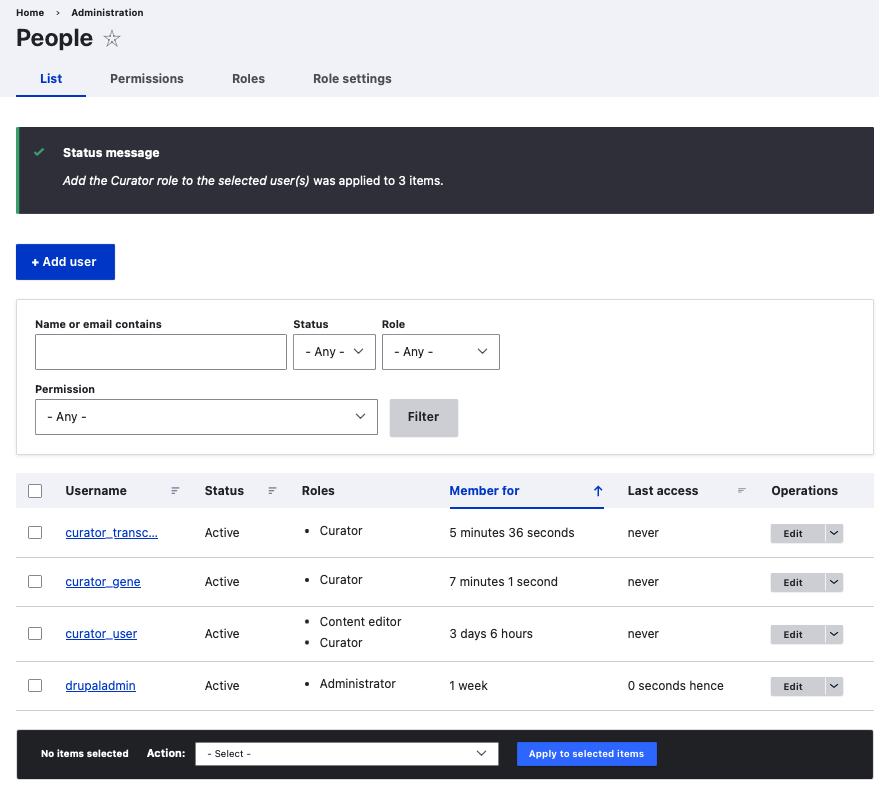
Click on dropdown next to Action -> select Add the Curator role to the selected users -> Apply to selected items.
All user names having prefix curator_ now have the role of Curator.
Home -> Administration -> People ->
Curator Roles are now assigned to the users under Roles.
Edit User’s Role
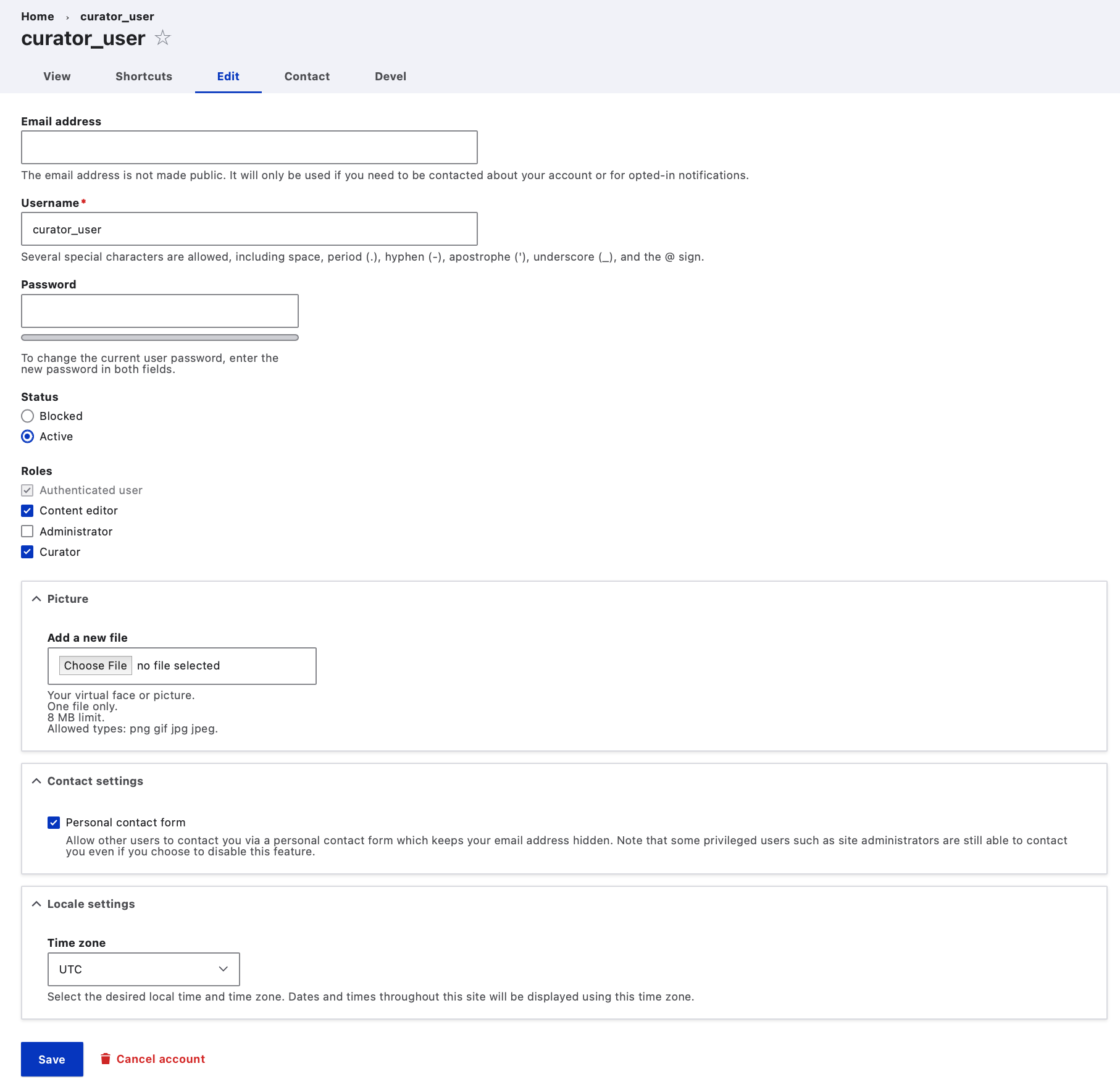
To Edit options for a user
Home -> Administration -> People -> curator_user -> Edit (under Operations column )
To remove the Content editor role for this user,
Uncheck Content Editor Role for example, make any other changes in this screen as required and Click Save.
Permissions for Role to define collaborative groups
From the top menu -> People -> Permissions
Click in applicable checkboxes for Content editor.
- The following Tripal content sections are available to assign permission options for each Role :
Block
Block Content
Comment
Configuration Manager
Contact
Contextual Links
Devel
Devel PHP
Field UI
File
Filter
Image
Node
Path
Search
Shortcut
System
Taxonomy
Toolbar
Tour
Tripal
Tripal Chado
Update Manager
User
Views UI
Some of the checkboxes are already checked are some are not changeable.
An administrator can change the default permissions for roles. For example, to change the recently created role of Curator,
From the top menu click on -> People -> Permissions.
In this screen individual permissions can be set for a Role by the administrator viewing the permissions checked for other roles.
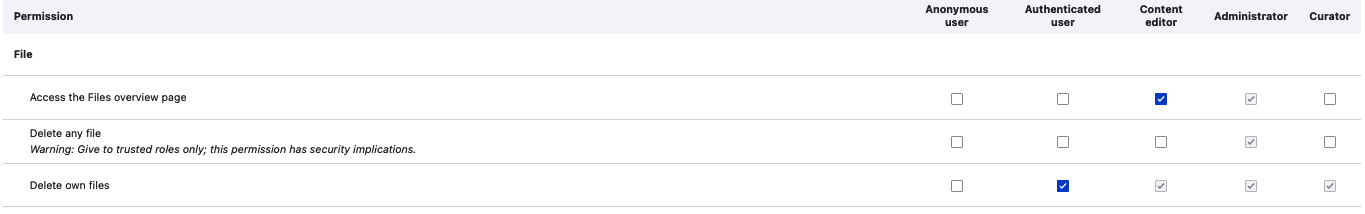
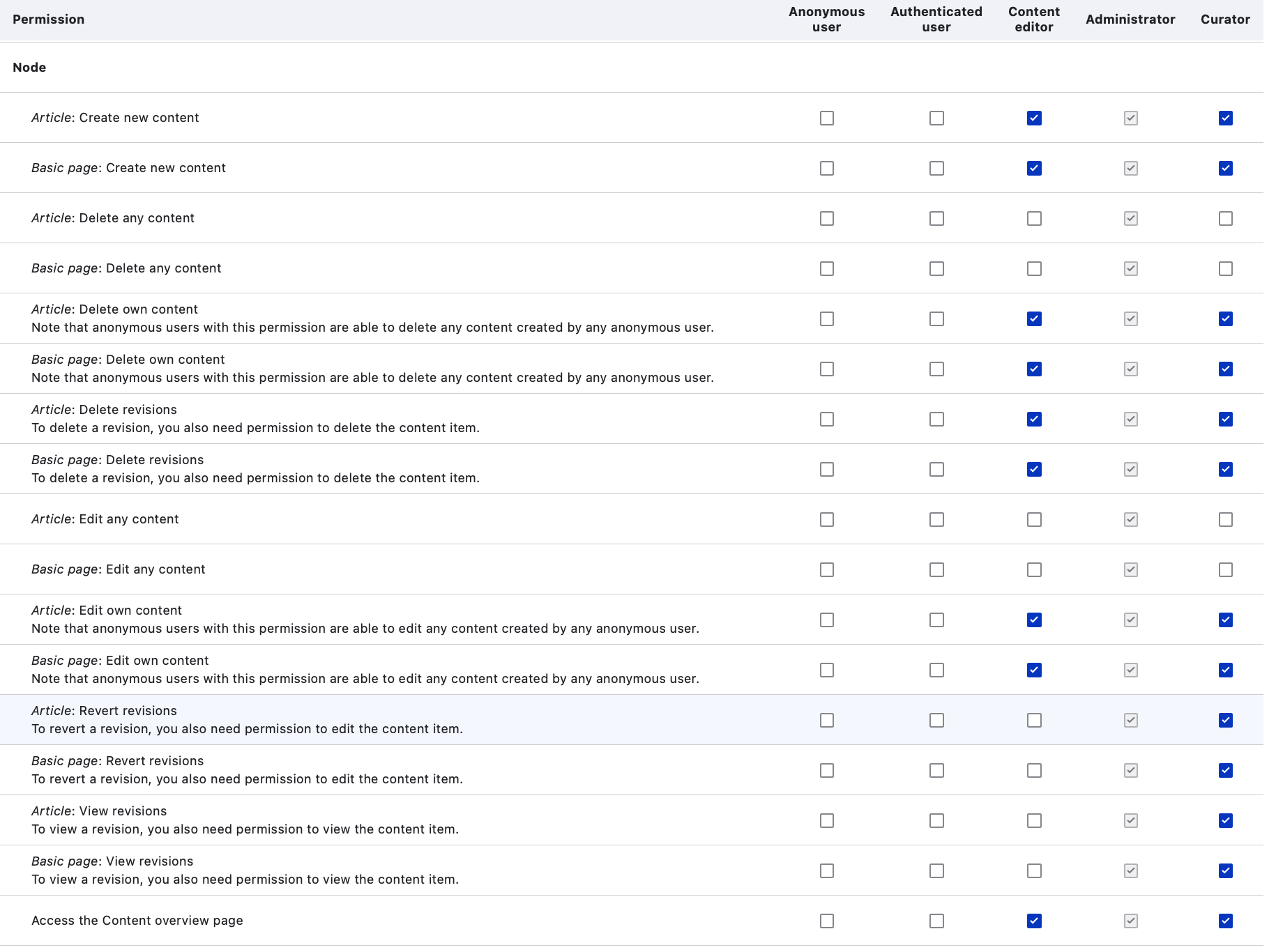
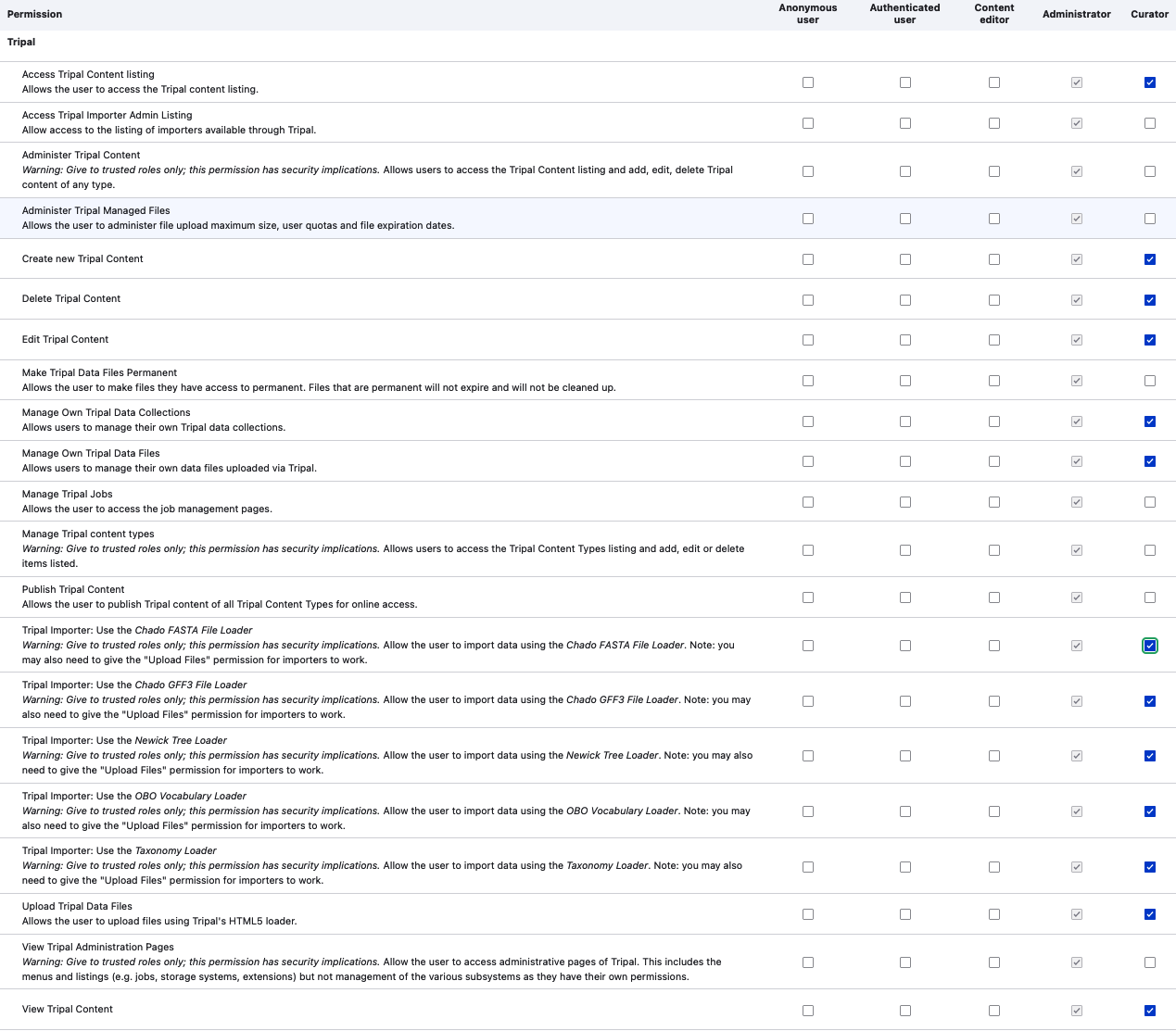
Here are some recommended permissions checked for the Role of the Curator in the File, Node and Tripal categories:
File permissions
Node permissions
Tripal permissions
Permissions checked for the Curator role shown in screenshots above help in editing, revising and reverting content in addition to several others not available to other Roles for importing content into Tripal, edit and maintain them.
Site administrators wanting to allow their curators to delete Tripal content can do so by applying the “Delete Tripal Content” permission. If their curator also imports data via available custom data importers like GFF3 importer they may want to assign the Tripal Importer permissions, publish and “Upload Tripal Data files”.
Permissions by Term
The Permissions by Term is a module that extends Drupal by providing functionality for restricting view access to single nodes via taxonomy terms. This module can be useful for Tripal users interested in creating, documenting and maintaining Ontologies, for example.
Taxonomy term permissions can be coupled to specific user accounts and/or user roles. It relies on the entities, which are shipped traditionally with Drupal core: taxonomy terms and nodes.
More information is available at https://www.drupal.org/docs/contributed-modules/permissions-by-term and https://www.drupal.org/project/permissions_by_term.
An example use-case in Tripal is Sub-editors working on a research publication. Collecting content together in a taxonomy term allows you to manage that content as a sub site and assign its own administrator. This is useful where you might need someone to produce lots of different types of content but only want them to be able to add it to a specific area of the website that is working on the publication.
Sub-communities within a membership organisation. The topics a membership organisation may cover can be very broad and individual members may only be interested in seeing content from a sub-selection of the areas it covers. The sub-community may have their own executive members who can contribute to the research topic or approve new members to their sub-community.