Controlled Vocabularies (CVs)
Controlled vocabularies are simply a collection of agreed upon names (knowns as terms) for items of interest. Within biology this may mean we have a controlled vocabulary describing the parts of a gene or the types of germplasm. And ontology is a specialized type of controlled vocabulary with additional structure including relationships between terms (i.e. the sequence ontology).
Tripal and Chado both use controlled vocabulary terms extensively to categorize data and metadata. The use of controlled vocabulary terms also allows both Tripal and Chado to be extremely flexible while also remaining very descriptive with rich metadata.
As you can see in the figure below, controlled vocabularies are collections of 1+ ID spaces and each ID Space is a collection of terms. The ID space provides the unique namespace for the term accession and a controlled vocabulary groups a bunch of similar terms.
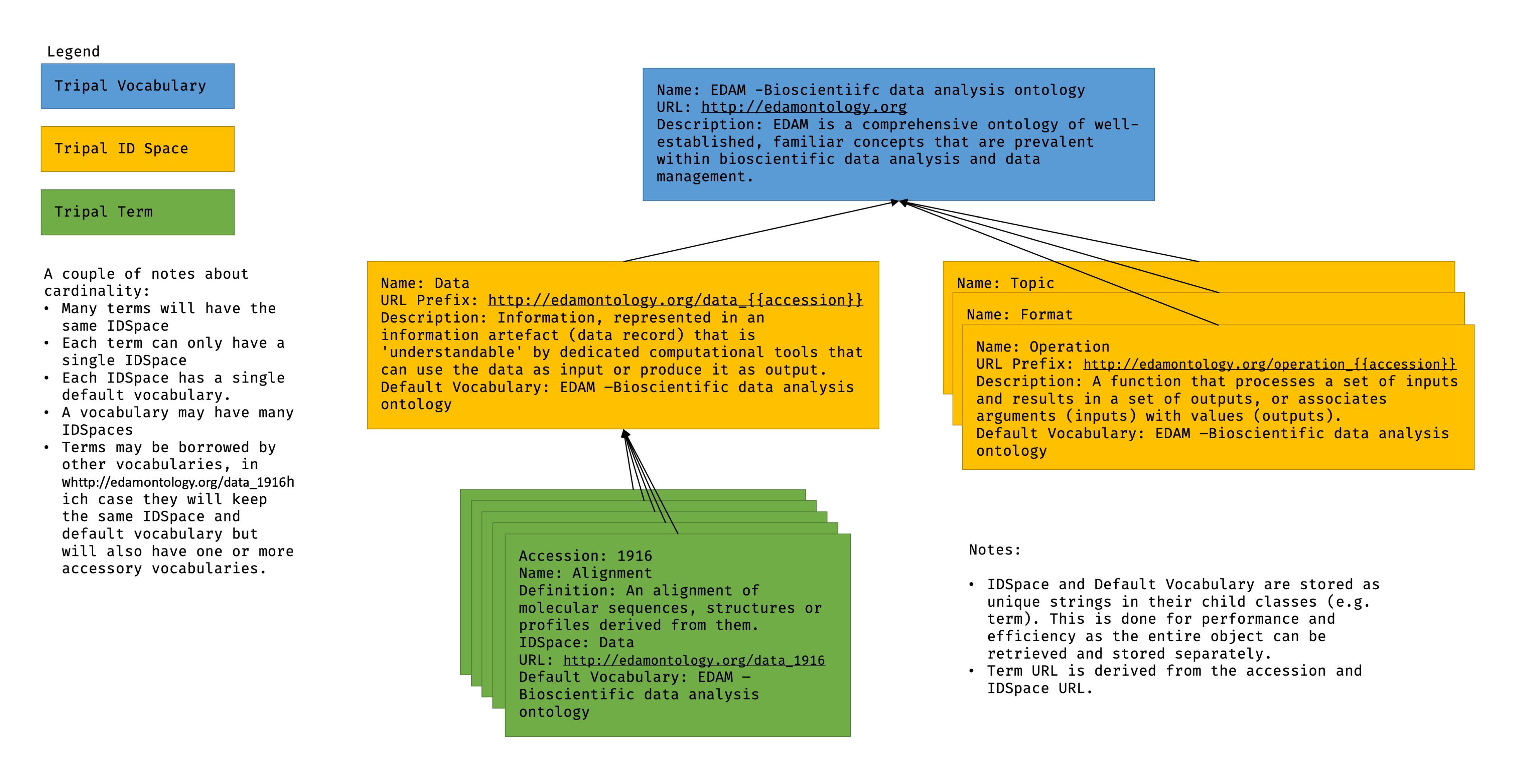
In Tripal 4, the Controlled Vocabulary API is designed to enable flexible backend storage and thus can be completely independent of Chado. That said, there is a default implementation of this API provided by the core Tripal Chado module that tightly integrates Tripal and Chado.
How are CVs used in Tripal?
Controlled vocabulary terms (CVTerms) are used to define Tripal Content Types. Additionally, all Tripal Fields are defined using a controlled vocabulary term. As such, all biological content managed by Tripal is associated with a categorizing controlled vocabulary term and each piece of metadata defining a single piece of content is also defined using a controlled vocabulary. This ensures that Tripal content is semantic web ready, as well as, ensuring it is well organized for both researchers and computer software.
Identifying a CVTerm
Before creating a new content type for your site you must identify a CVTerm that best matches the content type you would like to create. CVs are plentiful and at times selection of the correct term from the right vocabulary can be challenging. If there is any doubt about what term to use, then it is best practice to reach out to others to confirm your selection. The Tripal User community is a great place to do this by posting a description of your content type and your proposed term on the Tripal Issue Queue. Confirming your term with others will also encourage re-use across Tripal sites and improve data exchange capabilities.
The EBI’s Ontology Lookup Service is a great place to locate terms from public vocabularies. At this site you can search for terms for your content type. If you can not find an appropriate term in a public vocabulary or via discussion with others then you create a new local term within the local vocabulary that comes with Tripal.
Warning
Creation of local terms is discouraged but sometimes necessary. When creating local terms, be both precise and verbose in your description.
Retrieving Tripal Terms
Terms can be retrieved by
Using the Tripal Vocabulary Manager to search terms by name within a vocabulary.
Using the Tripal ID Space Manager to search terms by name or accession within an ID Space.
Using the Tripal ID Space Manager to get parent or child terms of an existing term.
Using the static TripalTerm::suggestTerms method to search by name across vocabularies and ID spaces.
Class |
Method |
Return |
Search Property |
IDSpace* |
Vocabulary* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TripalTerm |
suggestTerms+ |
array |
name |
No |
No |
TripalVocabulary |
getTerms |
array |
name |
No |
Yes |
TripalIdSpace |
getTerms |
array |
name |
Yes |
Yes |
TripalIdSpace |
getTerm |
TripalTerm |
accession |
Yes |
Yes |
TripalIdSpace |
getParent |
TripalTerm |
TripalTerm |
Yes |
Yes |
TripalIdSpace |
getChildren |
array |
TripalTerm |
Yes |
Yes |
Chado CV module
In Chado, controlled vocabularies and ontologies are stored in the CV Module. This module provides flexible storage of the individual terms, as well as, the relationships between them.